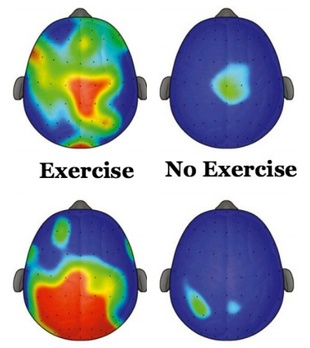
capacity and mental workload (P3 amplitude) during
cognitive tasks that require executive control in children
in the experiment and control groups. Red represents
the greatest amplitude, and blue the lowest.
(Hillman et al, Pediatrics/The Atlantic)
This morning the medical journalPediatrics published research that found kids who took part in a regular physical activity program showed important enhancement of cognitive performance and brain function. The findings, according to University of Illinois professor Charles Hillman and colleagues, "demonstrate a causal effect of a physical program on executive control, and provide support for physical activity for improving childhood cognition and brain health." If it seems odd that this is something that still needs support, that's because it is odd, yes. Physical activity is clearly a high, high-yield investment for all kids, but especially those attentive or hyperactive. This brand of research is still published and written about as though it were a novel finding, in part because exercise programs for kids remain underfunded and underprioritized in many school curricula, even though exercise is clearly integral to maximizing the utility of time spent in class.
Earlier this month, another study found that a 12-week exercise program improved math and reading test scores in all kids, but especially in those with signs of ADHD. (Executive functioning is impaired in ADHD, and tied to performance in math and reading.) Lead researcher Alan Smith, chair of the department of kinesiology at Michigan State, went out on no limb at all in a press statement at the time, saying, "Early studies suggest that physical activity can have a positive effect on children who suffer from ADHD."
Last year a very similar study in the Journal of Attention Disorders found that just 26 minutes of daily physical activity for eight weeks significantly allayed ADHD symptoms in grade-school kids. The modest conclusion of the study was that "physical activity shows promise for addressing ADHD symptoms in young children." The researchers went on to write that this finding should be "carefully explored with further studies."
(L. Brian Stauffer)
John Ratey, an associate professor of psychiatry at Harvard, suggests that people think of exercise as medication for ADHD. Even very light physical activity improves mood and cognitive performance by triggering the brain to release dopamine and serotonin, similar to the way that stimulant medications like Adderall do. In a 2012 TED talk, Ratey argued that physical exercise "is really for our brains." He likened it to taking "a little bit of Prozac and a little bit of Ritalin." As a rule, I say never trust anyone who has given a TED talk. But maybe in this case that's a constructive way to think about moving one's body. But not the inverse, where taking Ritalin counts as exercise.